People
Murtadha Alsayegh, Peter Vanegas, Abdullah Al Redwan Newaz, Leonardo Bobadilla, Dylan A. Shell
Motivation
The concept of multi-robot task allocation holds immense potential for identifying synergies between robots and optimizing their collective performance. While it is straightforward to achieve cooperation within a single organization, challenges arise when robots are competitors in a marketplace, safeguarding proprietary data and copyrights. However, limited cooperation among rivals, especially in the form of resource sharing and infrastructure utilization, can significantly reduce costs for all parties involved. Recognizing that competition and cooperation are not mutually exclusive, we address the crucial question of how to optimally allocate robots to tasks while upholding data privacy and confidentiality. Our approach tackles this question by:
- Implementing an auction-based assignment algorithm through secure multi-party computation operations, eliminating the need for a trusted auctioneer.
- By ensuring that no task valuations, utilities, positions, or related data are released, we provide precise and robust privacy guarantees that surpass existing methods.
- This innovative approach empowers multi-robot systems to collaborate effectively without compromising sensitive information, fostering a secure environment for cooperation in competitive landscapes.
For more details, you can check our paper
Details
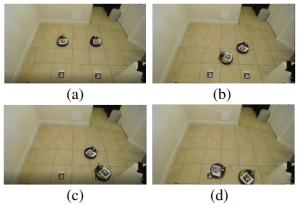
The below video demonstrate using a physical environment of two autonomous mobile robots performing a decentralized private auction.
A demonstration experiment shows the initial position
of the robots. At the end of the auction, each robot will be assigned a target.
Initially, both robots calculate their utilities, set their preferences, and perform the auction. Next, both robots start their motion toward their assigned targets. While motion, robot 2 detected an object and stops to avoid a collision using infrared
sensors. Finally, both robots reached their target positions