People
Abdullah Al Redwan Newaz , Murtadha Alsayegh, Tauhidul Alam, and Leonardo Bobadilla
Motivation
Efficiently exploring and gathering information from unknown spatial fields using decentralized mobile robots presents a significant challenge. Existing approaches that are limited to discrete domains and synchronous planning often struggle to scale well as the problem size increases. To address this, our motivation is to develop an incremental scalable motion planning algorithm that operates in continuous domains and employs an asynchronous communication strategy. The goal is to guide a team of cooperative robots to visit the most informative locations within a limited mission duration, where the informativeness is specified by a density function.
Details
Our proposed algorithm, called Asynchronous Information Gathering with Bayesian Optimization (AsyncIGBO), combines the principles of asynchronous Bayesian Optimization (BO) with decentralized reactive motion planning techniques. By efficiently sampling from the density function, AsyncIGBO enables effective exploration of the spatial field. The algorithm is designed to operate in a distributed manner, allowing the robots to make autonomous decisions based on local observations and communicate asynchronously. This approach facilitates efficient multi-robot information gathering activities, overcoming the limitations of traditional methods.
To support our algorithm’s efficacy, we provide a theoretical justification through an asymptotic no-regret analysis concerning a known spatial field. This analysis demonstrates the algorithm’s ability to make informed decisions and adapt to changing environments over time. Furthermore, we extensively validate our proposed algorithm through simulations and real-world experiments involving multiple robots, ensuring its practical applicability and reliability.
By introducing the AsyncIGBO algorithm, we aim to advance the field of decentralized mobile robot information gathering. Our approach offers enhanced efficiency and effectiveness, allowing robots to explore and collect valuable information from unknown spatial fields in a scalable and adaptable manner. The outcomes of our research have the potential to benefit various domains that rely on decentralized robotic systems for data collection, including environmental monitoring, surveillance, and exploration.
In this project, we make four contributions:
- Propose an Asynchronous Information Gathering with Bayesian Optimization (AsyncIGBO) algorithm to choose the next informative samples for robots subject to their observed knowledge
- Estimate the unknown density function from gathered samples with independently exploring multiple robots
- Generate a distributed control law in continuous domains while considering realistic robotic resource and motion constraints
- Theoretically analyze the asymptotic no-regret properties of our algorithm with respect to a known spatial field
For more details, you can check our paper
The below video demonstrates using a decentralized multi-robot information gathering simulation and physical environment of two autonomous mobile robots performing a decentralized private auction.
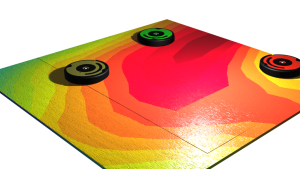
Decentralized multi-robot information gathering simulation: Three robots starting with random initial states are
visiting the most informative regions on a spatial field while avoiding not only static obstacles but also inter-robot collisions.
Physical experiment with multiple robots: Two robots are collecting information from a projected spatial field.